Your CBD Extract Wholesaler
Cannabinoids / Chemistry
- 1
- 2
Cannabinoids / Chemistry
The hemp plant (Cannabis Sativa L) is made up of a group of molecules. These are cannabinoids. However, the plant also contains many other substances, such as terpenes and even flavonoids. Together, they enable cannabis or hemp to deliver the effects it's known for. In this part of our blog, you'll find out all you need to know about these components, their actions and interactions.
What's a cannabinoid?
What's a cannabinoid?
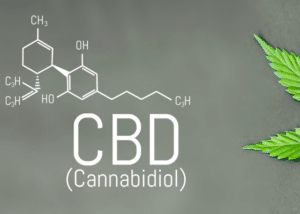
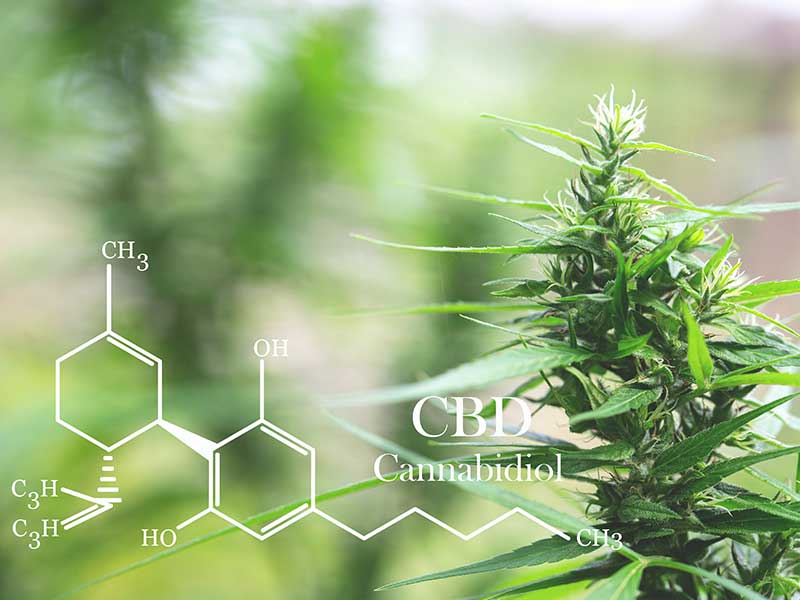
A cannabinoid is the name given to the molecules that make up the hemp plant. To date, nearly 500 are known, each with its own particularity and acting differently from the others. The THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the best known, notably for its psychoactive action. The CBD (cannabidiol) is the second best known, since it is currently at the heart of debate for its supposed benefits (on stress, anxiety, pain, etc.). Other cannabinoids, such as CBG (cannabigerol) and CBN (cannabinol), are also much appreciated by scientists, who are trying to determine the relationship between each of them. In fact, when a product is "full spectrum", i.e. contains the entire cannabinoid spectrum, a still poorly understood chemistry takes place: theentourage effect. Cannabinoids act in concert, supporting each other and multiplying their effects. Present in large quantities, they are extremely important. Although we know the structure of the cannabis plant, we still need to determine the action and effects of these natural molecules.The cannabinoid CBD
Visit CBD is the abbreviation used for cannabidiol. It's a cannabinoid, naturally present in the cannabis plant. Its use is varied. Indeed, after extraction of the cannabinoid by Supercritical CO2It can be processed and used in CBD oils, CBD resins, infusions and hemp flowers. CBD is a cannabinoid often presented as having therapeutic properties. In particular, it is consumed to help treat a number of ailments, such as:- Anxiety, stress, depression and sleep disorders;
- Pain and inflammation;
- Addictions.
The cannabinoid THC
Visit THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is one of the best-known cannabinoids. It is responsible for psychoactive effects associated with the consumption of the same cannabis plant. Its use, whether by ingestion, topical application, sublingual use or combustion, produces an intoxicating high. This is accompanied by hunger (cravings) and an intense feeling of relaxation. The THC can also cause side effects such as short-term memory disturbances, confusion, anxiety and paranoia. This cannabinoid is now being studied for its potential therapeutic effects. For example, it could help treat pain and nausea in cancer patients. It could also improve appetite in people with serious disorders such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's, etc. However, because of its psychoactive action, its use is subject to strict regulations. For example, THC is illegal in many countries. In France, for example, this cannabinoid is listed as a narcotic.The cannabinoid CBG
Cannabinoid naturally present in the hemp plant, CBG, for cannabigerol, is one of the precursor cannabinoids. Through various chemical and natural reactions, it is transformed into other cannabinoids such as THC and CBD. CBG is present in relatively small quantities in most cannabis strains, but it is extremely important. By cultivating genetically modified plants, however, it is possible to obtain richer CBG varieties. It is thought that CBG has therapeutic properties and has been studied for its potential effects on a variety of disorders, including inflammation, pain and anxiety. However, there is still little research into the effects and potential benefits of CBG, and many aspects of its effects on human health remain to be elucidated.
What are the effects of cannabinoids?
What are the effects of cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids have a wide range of actions. In fact, they do not all act in the same way on the body, nor do they all serve the same purpose. As we have seen THC alone has a psychotropic action. CBD, on the other hand, has a positive effect on stress and sleep, while CBG has a pain-relieving effect, helping to relax muscles and combat aging of the body. What about terpenes and flavonoids? These molecules also play an interesting role, providing the cannabis plant with all its aromas and notes. They enable a variety to develop and eventually obtain its characteristics. The result is a quality product! Finally, all these molecules act on the endocannabinoid system, enabling a product rich in CBDto have the actions that are attributed to it. Without cannabinoids terpenes or the flavonoidsFor example, consuming a product based on hemp or derived from the cannabis plant would be pointless in the end, as it would be bland in the mouth and would not present any form of potentially interesting action for the body.
Is scientific research being done to understand the chemistry of CBD?